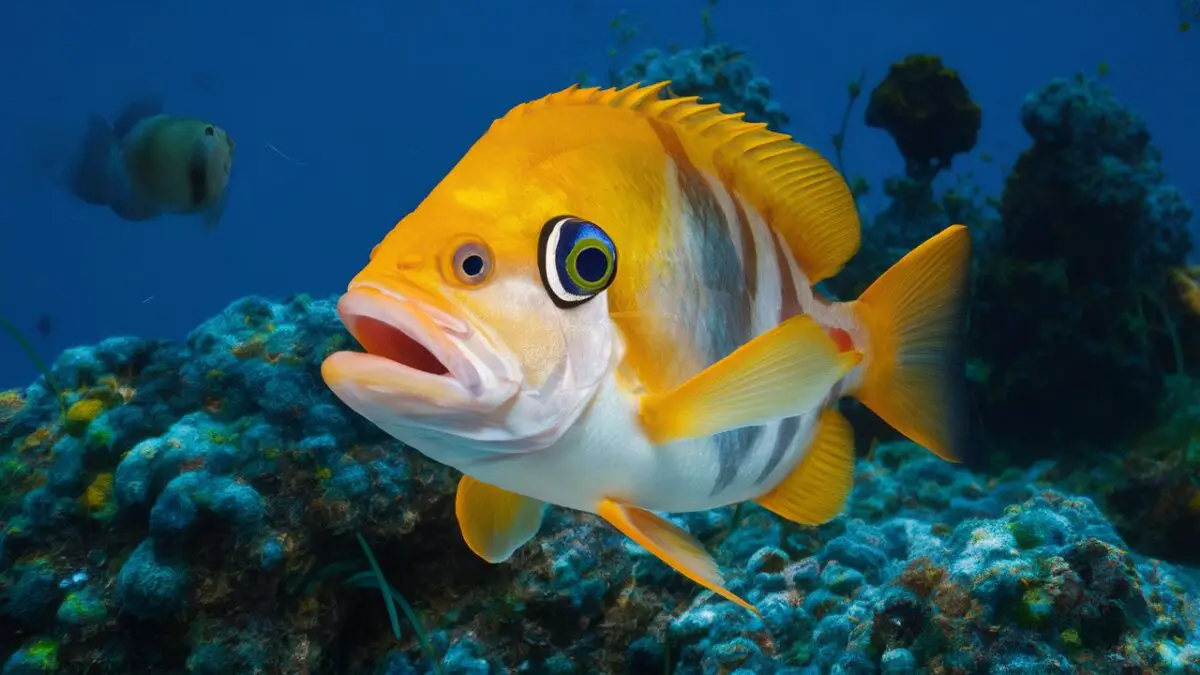
Considering the Behavioral Lens of Fish: with their dazzling array of colors and diverse species, have captivated the human imagination for centuries.
The complex realm of fish behavior, which extends beyond their visual allure, captivates both scientists and amateurs equally.
This essay will study the fascinating behaviors displayed by these aquatic species by delving into the depths of the undersea universe.
Fish behavior is fascinating because of its intricate social systems.
Several fish species participate in complex social interactions, building alliances and hierarchies, in contrast to the common misconception that they are solitary animals.
Consider the clownfish, which develops symbiotic partnerships and displays distinct communication patterns with sea anemones.
In addition to helping fish survive, these actions demonstrate how remarkably adaptive fish are in a variety of environments.
Fish migration is a phenomenon that adds even more interest to their activity.
Certain animals can cover hundreds of miles while making very accurate navigational maneuvers across ocean currents.
Their migratory movement not only demonstrates their ability to navigate, but it also distributes nutrients and controls population density, which is essential to preserving ecological balance.
Investigating fish behavior also demonstrates their incredible capacity for problem-solving.
Fish have a degree of intellect that defies conventional beliefs, as seen by some species’ use of tools and intricate hunting techniques.
Researching these behaviors helps us better understand marine ecosystems and highlights the importance of conservation efforts to save these amazing animals and the delicate balance of their underwater environment.
Brushless RC Boat 40+MPH, Remote Control Boat for Adults Kids Enthusiasts

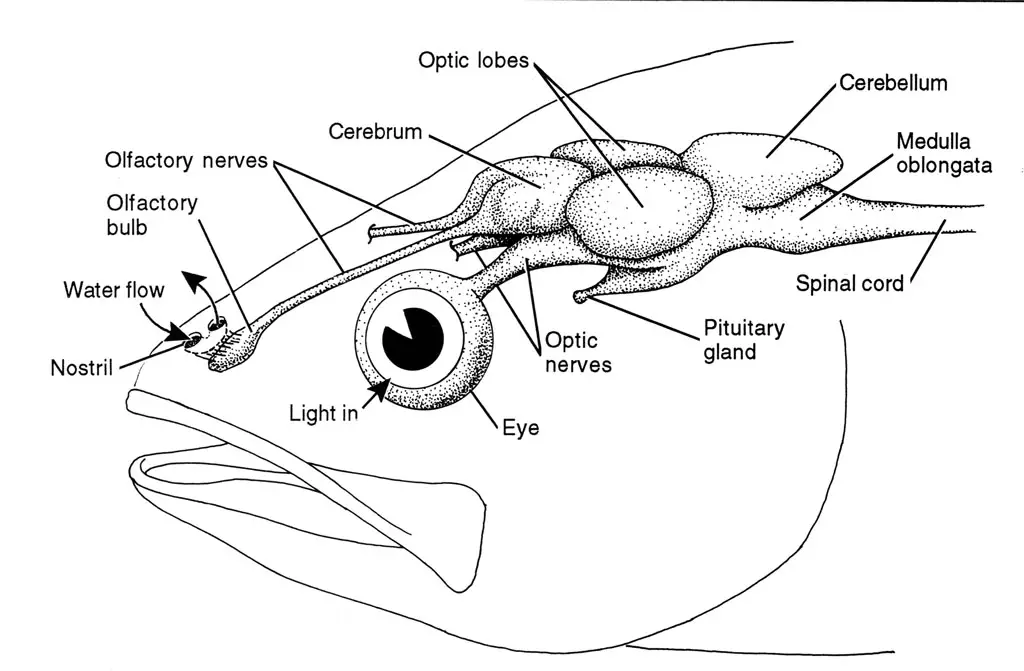
Basics of Fish Behavior
Recognizing a fish’s innate patterns is the first step towards understanding their behavior.
These animals use a collection of behaviors developed over millennia to navigate their watery environments, including complex mating rituals and hierarchical social structures.
The environment greatly influences fish’s interactions with their surroundings and with one another.
Fish behavior is fascinating because it shows a fascinating story of survival and adaptation.
The intricate mating rituals not only aid in reproduction but also demonstrate the deep-rooted evolutionary creativity within their species. They are a dance of colors and motions.
Hierarchical social systems govern fish communities, establishing cooperation and dominance among individuals even beyond the level of reproduction.
Millennia of evolution have refined these habits to maximize their chances of prospering in a variety of aquatic habitats.
Environmental factors such as water temperature, current intensity, and resource availability carefully shape these behavioral patterns.
Fish, in concert with their environment, effectively become the choreographers of their underwater world.
Understanding these actions not only reveals the mechanisms underlying their survival, but also emphasizes the fine equilibrium necessary for marine environments’ well-being and durability.

Factors Affecting Fish Behavior
The primary determinants of fish behavior that are dynamic include temperature, water quality, and eating patterns.
The intricate interweaving of these components defines the rhythm of aquatic life, resulting in a rich tapestry.
Beyond these basic elements, this ecological dance becomes much more intricate when one learns about the mysterious details of fish reproductive cycles.
Various hormonal triggers, environmental signals, and species-specific adaptations influence the amazing phenomenon of fish reproduction.
Specific temperature thresholds trigger certain fish species, while seasonal fluctuations coordinate the reproductive activities of others.
The complicated network of connections that governs fish reproduction highlights the delicate balance needed for a flourishing aquatic ecosystem.
Variables like changes in water temperature can greatly impact the success and timing of spawning episodes.
Water quality, which includes nutrient levels and contaminant content, further influences the health and viability of fish progeny.
The availability of suitable nesting locations and complex courting customs among fish species also play a role in the overall reproduction dynamics.
To put it simply, understanding fish behavior’s complexity entails deciphering the secrets of their mating habits, which provide a deep window into the complex dynamics of aquatic environments and the fragile balance necessary for their survival.

Unusual Fish Behaviors
It appears that fish have no shortage of theatricality. Extensive displays are a part of mating rituals, and territorial actions may be just as fascinating as a nature documentary.
Fish use a variety of body motions and audible signals to communicate, which adds to the attraction of their activities.
Beyond these unique features, fish also demonstrate extraordinary intellect and problem-solving abilities, upending the conventional belief that they are only instinctually driven animals.
Recent studies have shown that some fish species possess cognitive capacities, including the ability to learn, remember, and even use tools.
Certain animals, for example, show signs of social learning, can identify themselves in mirrors, and can maneuver through intricate mazes.
Moreover, fish species’ remarkable variety adds to the diversity of their behavioral repertoire.
Every habitat offers a different display of aquatic activities, from the vivid coral reefs home to colorful tropical fish to the dark, enigmatic depths where bioluminescent animals travel at night.
The aquatic environment presents itself as a stage for a captivating variety of plays as we go further into the study of fish behavior, illustrating that under the surface, a rich tapestry of life and interaction emerges.

How Humans Influence Fish Behavior
Fish move gracefully through their aquatic environments, but human activity has the potential to upset these fragile ecosystems.
Our influence is significant, ranging from habitat degradation to overfishing. Understanding these factors is essential for responsible environmental management.
Overfishing threatens the equilibrium of entire marine ecosystems, driven by a rising global demand for seafood.
Large-scale fishing operations frequently deplete fish populations faster than they can naturally replenish, which leads to the collapse of fisheries and the disappearance of biodiversity.
Habitat degradation, primarily due to activities like coastal development, pollution, and climate change, further endangers aquatic ecosystems.
Numerous marine species depend on mangroves, coral reefs, and estuaries as crucial fish nurseries and habitats.
Damage to or elimination of these habitats results in a decrease in fish populations, which affects both the natural balance and the way of life for those who depend on fishing.
A comprehensive strategy that includes habitat conservation, international collaboration, and sustainable fishing methods is required to overcome these issues.
We must implement and uphold laws that restrict overfishing, protect important ecosystems, and promote responsible consumption to ensure the resilience and health of our seas.
It is our responsibility as stewards of our planet to acknowledge the interdependence of our activities and work toward peaceful cohabitation with the various marine life forms that call our waters home.
Brushless RC Boat 40+MPH, Remote Control Boat for Adults Kids Enthusiasts
The Curious Case of Fish Memory
Breaking the idea that fish only have a short memory span, a new study has shown unexpected results that go against accepted knowledge.
Fish, contrary to common opinion, have a very complex memory system that can perform remarkable feats of learning and adaptability.
Scientists and fans alike are becoming more and more fascinated with the intricacy of fish memory.
Research suggests that a number of fish species possess cognitive capacities beyond instinctive behavior.
Certain fish, for example, are able to identify their tank mates, recall food regimens, and even make very accurate maze navigation.
This implies a degree of memory recall that transcends basic survival instincts and indicates a more sophisticated comprehension of their surroundings.
Moreover, studies on the neurological elements of fish memory have shown brain pathways that support fish cognitive functions.
The results refute the myth that fish are mindless animals and instead present them as sentient entities who can adjust to their environment by drawing on their prior experiences.
Essentially, the growing body of research on fish memory emphasizes the necessity of reconsidering how we view aquatic life and the cognitive abilities that these sometimes underappreciated animals possess below the surface.

Fish Intelligence: More Than Meets the Eye
Fish have problem-solving skills that go beyond memory, defying theories of aquatic intelligence.
Investigating fish cognitive abilities reveals a complexity that calls for a reassessment of our knowledge of these animals.
Recent studies have shown amazing examples of some fish species using tools, such as breaking open shellfish with pebbles or building nests out of different materials.
These actions point to hitherto unknown levels of cognitive flexibility and adaptation in fish.
Furthermore, social structures and communication techniques found in certain species allude to a higher degree of intellect.
For instance, studies have shown that some coral reef fish species can identify individual fish within their group and employ coordinated hunting strategies.
These intricate social activities dispel myths about fish’s alleged shallow intellect and cast doubt on the nature of fish cognition.
These results make it necessary to reevaluate the moral issues related to fish in a variety of settings, including aquaculture operations and conservation initiatives.
Understanding fish’s mental capacities leads to a more sympathetic attitude toward their well-being, as well as an increased respect for their significance in ecosystems.
Deeper exploration of the subtleties of fish intelligence reveals that the aquatic world is full of surprises and complexities that challenge conventional wisdom.
Considering the Behavioral Lens of Fish

Ethical Considerations in Observing Fish Behavior
It is imperative that we observe fish in an ethical manner when we are in awe of their underwater beauty.
The survival of these animals and their habitats depends on responsible aquarium maintenance and conservation initiatives.
Beyond simple curiosity, ethical fish observation is a dedication to comprehending and protecting aquatic environments.
To achieve this, academics and aquarium hobbyists should place equal emphasis on sustainable methods and promote captive breeding initiatives rather than harvesting wild fish for aquarium commerce.
Furthermore, efforts should focus on habitat protection because aquatic life depends on the health of ecosystems.
The delicate balance of whole marine ecosystems, as well as the preservation of individual species, rely heavily on conservation efforts.
The public, environmental organizations, and government authorities can support the establishment and enforcement of regulations that protect marine environments from pollution, overfishing, and habitat degradation.
We can help preserve these aquatic wonders for future generations to enjoy by raising awareness of the significance of ethical fish observation and actively taking part in conservation initiatives.
By doing this, we respect the inherent worth of marine life as well as our duty as ocean stewards.

The Joy of Fish Watching
Seeing fish is enjoyable for reasons other than scientific curiosity.
There are several health benefits to seeing fish, whether they are in the wild or in an aquarium.
It’s an opportunity to establish a deep connection with nature.
Their rich ecosystems, vivid colors that dance beneath the water’s surface, and fluidity of movement all captivate us.
You get a sense of calm as you watch these aquatic creatures traverse their environment; it’s like taking a brief break from the daily grind.
There’s a contemplative rhythm that calms the mind in the silent waltz of scales and fins.
According to studies, looking at fish can help people feel more at ease and aware by lowering their stress and anxiety levels.
It serves as a reminder of the delicate equilibrium that exists in the world under the waves, as well as a type of natural treatment.
Whether you’re staring into the glass walls of an aquarium or sitting beside a calm pond, the aquatic world provides a different viewpoint that promotes reflection and introspection.
It’s more than just watching fish in these times; it’s about reestablishing a relationship with nature and, as a result, experiencing a fresh appreciation for the beauty all around us.

Tools for Fish Behavior Observation
The study of fish behavior has undergone a revolution because of the incorporation of cutting-edge technology, which has given scientists and fans unparalleled access to the subtleties of aquatic life.
Underwater cameras are at the forefront of this technological revolution, serving as windows into the secret lives of fish below the surface of the water.
These cameras, equipped with high-resolution lenses and sophisticated imaging capabilities, capture the subtleties of fish activity in their natural environments.
Because of this, scientists can now clearly study mating rituals, eating habits, and territorial behaviors up close.
Initiatives related to citizen science have become a potent force in broadening the field of marine studies, surpassing the purview of professional research.
Thanks to these initiatives, individuals with or without scientific training can now actively participate in larger research endeavors.
Volunteers and concerned individuals may help with data collection, fish population monitoring, and even recording odd behavior.
In addition to increasing the amount of data that is available, this cooperative strategy encourages community involvement in the preservation of aquatic habitats.
All things considered, the convergence of technology development and public participation has revolutionized our comprehension of fish behavior.
This harmonious blend fosters a sense of collective responsibility for the preservation of our aquatic habitats while also advancing scientific understanding.
Brushless RC Boat 40+MPH, Remote Control Boat for Adults Kids Enthusiasts

Challenges in Studying Fish Behavior
Modern tracking systems, in addition to underwater cameras, have completely changed our comprehension of fish behavior.
These devices, equipped with GPS and additional sensors, allow researchers to monitor the migratory patterns, eating habits, and environmental preferences of various fish species.
Because of this, researchers are able to gather priceless information that clarifies the complexities of marine ecosystems.
Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence algorithms in data analysis has sped up the processing of enormous volumes of data, making the discovery of behavioral patterns more effective.
Citizen scientific projects have also adopted technology, encouraging a team-based approach to fisheries research.
Enthusiasts may record fish sightings, submit photos, and even participate in virtual tagging exercises using smartphone applications and internet platforms.
In addition to including a larger audience in the scientific process, this inclusive methodology creates a large database that helps researchers examine fish populations in various geographic locations.
The convergence of technological advancements and public participation not only improves our understanding of fish behavior but also highlights the significance of teamwork in maintaining aquatic environments.
The celebration of the convergence of technology and citizen science opens up new opportunities for accessing the underwater environment and encourages everyone to take responsibility for the varied and delicate marine life.

Conservation Implications
A better understanding of fish behavior implies a need to protect their environments.
Encouraging sustainable fishing methods and conservation efforts is essential to preserving the fragile equilibrium of aquatic environments.
The complex interactions that different fish species have with their surroundings highlight the importance of careful stewardship.
To avoid overexploitation and guarantee the long-term health of fish populations, it is crucial to implement and promote sustainable fishing practices, such as habitat preservation and selective harvesting.
Conservation efforts are essential to protecting aquatic environments from the various dangers they encounter.
It is critical to make efforts to create marine protected zones and carry out ethical resource management plans.
Successful conservation initiatives must involve local populations and promote international cooperation.
We can encourage group action and a sense of environmental responsibility by bringing attention to the need to protect fish habitats.
In the end, maintaining habitat and engaging in sustainable fishing are acts that benefit the health of our world.
It supports the livelihoods of populations that depend on fishing, as well as the biodiversity of aquatic environments.
While we acknowledge and appreciate the progress made in our understanding of fish behavior, let us also recognize the need to preserve and value the environments that these fascinating animals call home.

Conclusion
Every fresh observation broadens our understanding of the ever-changing story of fish behavior.
Recent investigations have revealed the subtleties of their communication, revealing a complex language of gestures, body movements, and even color changes.
These findings challenge accepted beliefs about fish cognitive capacities and highlight the intricacy of fish communities, in addition to their extraordinary memory and astonishing problem-solving ability.
While we enjoy the spectacle of fish, mesmerized by their multicolored displays and complex social structures, let us also pledge to support the conservation initiatives required to protect their underwater habitat.
The degradation of habitats and overfishing are two examples of how human activity threatens aquatic environments.
We can help preserve the amazing and varied life below the surface by encouraging sustainable behaviors, creating marine protected areas, and increasing public awareness of the vulnerability of underwater habitats.
As our comprehension of fish behavior expands, so too should our dedication to maintaining a healthy, balanced aquatic ecosystem for future generations.
FAQs
Do fish have feelings?
While it’s challenging to gauge emotions in fish, studies suggest they can experience stress and pain.
Can fish recognize humans?
Some species of fish can indeed recognize individual humans, especially those regularly present in their environment.
How long is a fish’s memory?
Contrary to the popular myth, some fish species have demonstrated memory spans of several months.
What’s the most intelligent fish species?
The octopus is often considered one of the most intelligent among aquatic animals, although it’s not a fish.
How can I contribute to fish conservation?
Supporting sustainable fishing practices, participating in clean-up efforts, and staying informed about conservation initiatives are impactful ways to contribute.
Hooked on Tech: Exploring the latest Fishing Gadgets that Anglers swear by.
In the realm of angling, where tradition and technology often converge, a new wave of fishing gadgets has emerged, transforming the way anglers approach their craft.
From advanced fish finders to smart bait systems, these innovations have not only revolutionized the fishing experience but have also garnered a loyal following among anglers worldwide.

























