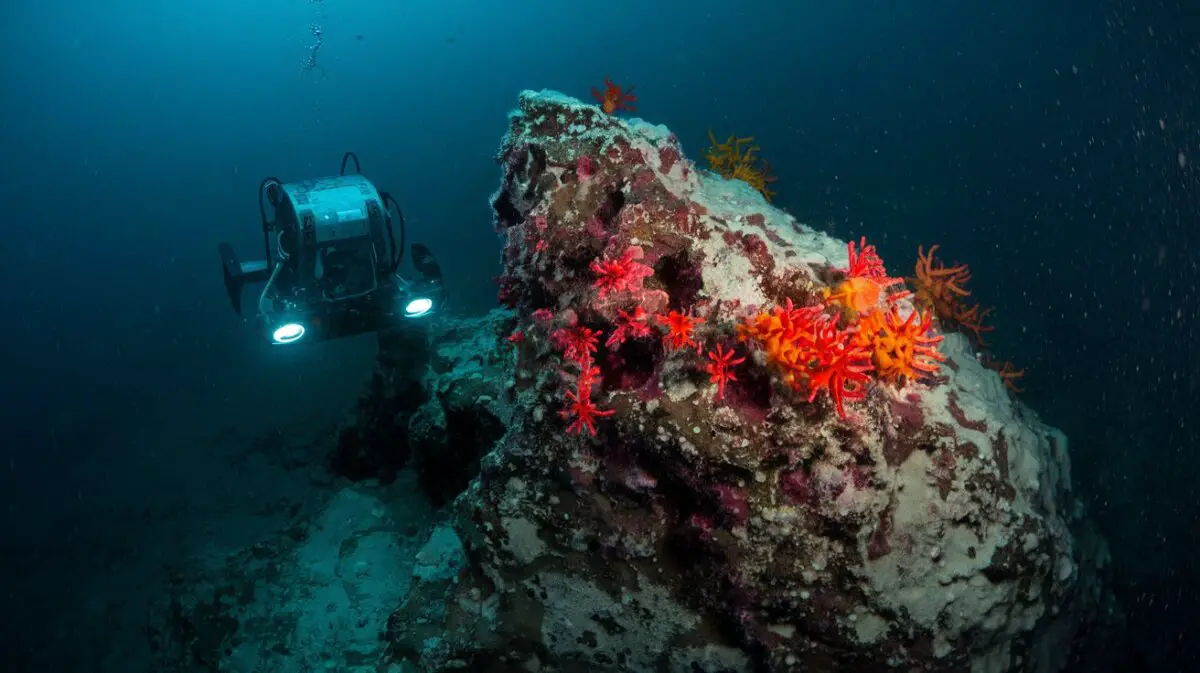
Deep-Sea Exploration, covering over half of the Earth’s surface, is a largely unexplored and enigmatic environment characterized by extreme pressure, complete darkness, and near-freezing temperatures. Despite these harsh conditions, it is home to a vast array of life forms and holds numerous secrets waiting to be uncovered. The allure of deep-sea exploration has long fascinated humans, promising the discovery of new species, the uncovering of ancient shipwrecks, and the revelation of the Earth’s history.
The deep sea is inhabited by a diverse range of unique and extraordinary creatures, including bioluminescent jellyfish and giant squid, captivating the imagination of both scientists and adventurers. Moreover, the deep sea holds significant geological importance, as it provides valuable insights into the Earth’s past and present. The ocean floor features hydrothermal vents, underwater volcanoes, and vast mountain ranges, all of which play a crucial role in shaping the planet’s geology and climate.
By exploring the deep sea, scientists can closely examine these features and gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s internal dynamics. Recent technological advancements have enabled the exploration of the deep sea in previously unimaginable ways, leading to a surge in discoveries and a renewed interest in this mysterious realm.
Key Takeaways
- Deep-sea exploration reveals a fascinating world with unique discoveries and mysteries waiting to be uncovered.
- Recent discoveries in deep-sea exploration have provided valuable insights into the biodiversity and ecosystems of the deep ocean.
- Cutting-edge technologies such as remotely operated vehicles and autonomous underwater vehicles are revolutionizing deep-sea exploration.
- Deep-sea exploration poses challenges and risks, including extreme pressure, darkness, and the potential impact on fragile deep-sea ecosystems.
- Deep-sea exploration is crucial for scientific research, providing valuable data for understanding climate change, biodiversity, and the origins of life on Earth.
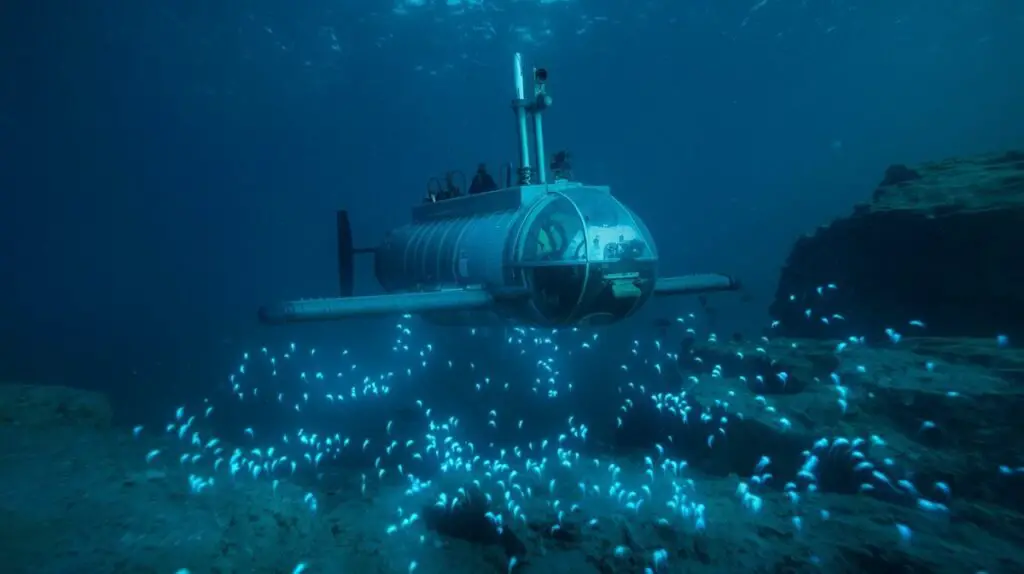

Uncovering the Mysteries of the Deep: Recent Discoveries
Hydrothermal Vents: A Hub of Unique Life Forms
One of the most significant findings has been the discovery of hydrothermal vents, which are home to some of the most unique and bizarre life forms on the planet. Located along mid-ocean ridges, these vents release superheated water rich in minerals, supporting a thriving ecosystem of tube worms, giant clams, and other strange creatures.
Seamounts: Biodiversity Hotspots
Another major discovery has been the identification of vast underwater mountain ranges known as seamounts. These underwater mountains are hotspots of biodiversity, providing a habitat for a wide variety of marine life, including corals, sponges, and fish. Seamounts also play a crucial role in ocean circulation and nutrient cycling, making them an important focus of scientific research.
Uncovering the Ocean’s Secrets: Archaeological Treasures
In addition to biological discoveries, deep-sea exploration has also led to the discovery of ancient shipwrecks, lost cities, and other archaeological treasures that shed light on human history and culture. These discoveries have not only captured the public’s imagination but have also provided valuable insights into the past and the ways in which humans have interacted with the ocean throughout history.
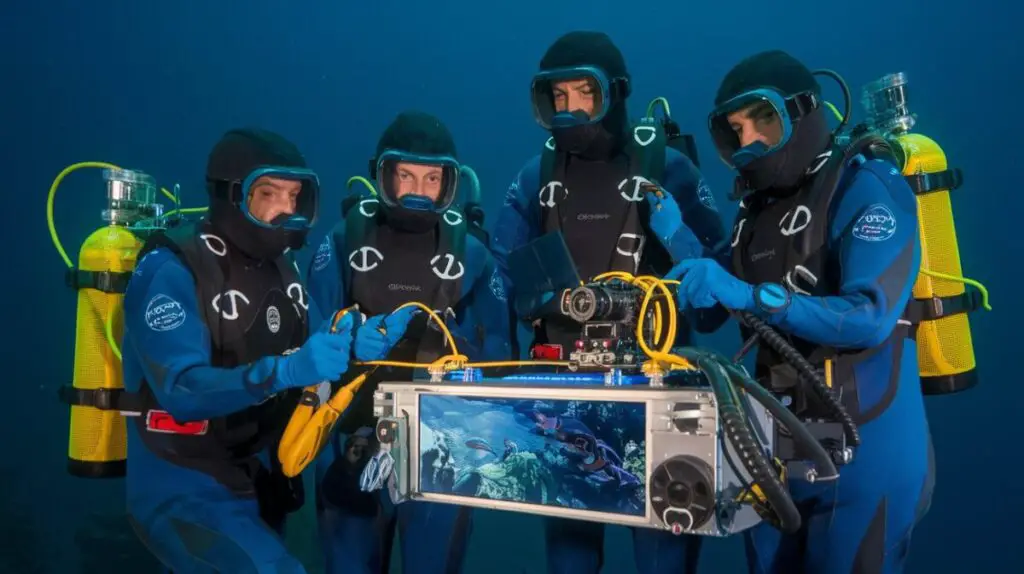

Cutting-Edge Technologies Used in Deep-Sea Exploration
The exploration of the deep sea would not be possible without the use of cutting-edge technologies that allow scientists to study this remote and inhospitable environment. One of the most important tools in deep-sea exploration is the remotely operated vehicle (ROV), which is a robotic submarine equipped with cameras, sensors, and manipulator arms that allow it to explore the ocean floor and collect samples. ROVs are controlled from the surface by a team of scientists and engineers who use live video feeds to navigate through the depths and study the marine life and geological features they encounter.
These vehicles have revolutionized deep-sea exploration by allowing researchers to access areas that were once unreachable and to conduct detailed studies of the ocean floor. Another key technology used in deep-sea exploration is the autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV), which is a self-propelled robot that can navigate through the ocean without human intervention. AUVs are equipped with a variety of sensors and instruments that allow them to collect data on water temperature, salinity, and currents, as well as to map the seafloor and study marine life.
These vehicles are particularly useful for conducting large-scale surveys of the ocean floor and for studying areas that are too deep or too dangerous for human divers to access. In addition to ROVs and AUVs, deep-sea exploration also relies on advanced sonar systems, satellite imaging, and other remote sensing technologies that provide valuable data on the ocean’s depths. These technologies have greatly expanded our ability to study the deep sea and have led to numerous groundbreaking discoveries in recent years.
Deep-Sea Exploration
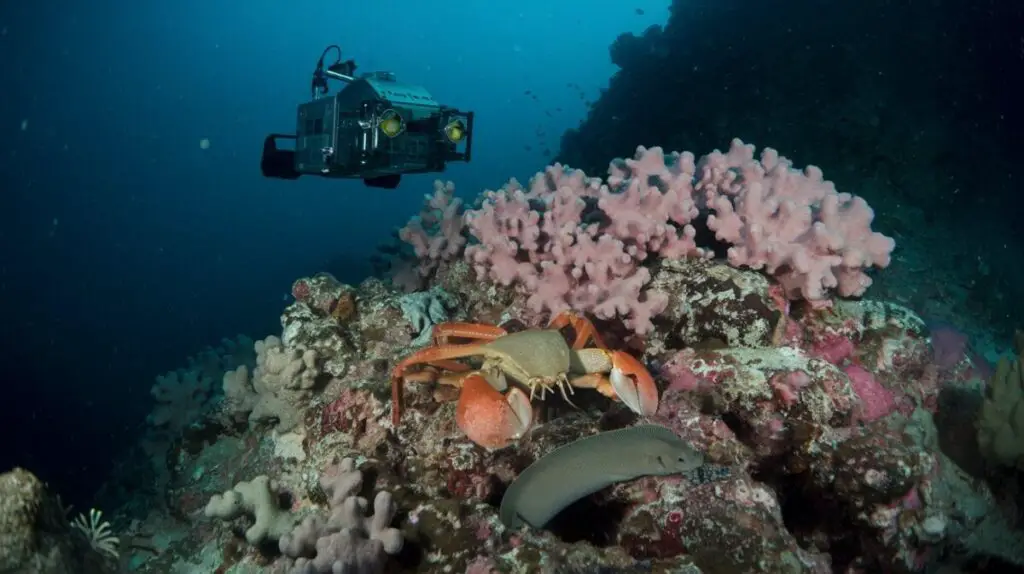

Challenges and Risks of Deep-Sea Exploration
| Deep-Sea Exploration: Discoveries and Technologies | |
|---|---|
| Depth of exploration | 10,000 meters |
| Number of new species discovered | Over 10,000 |
| Technologies used | ROVs, AUVs, Submersibles |
| Exploration areas | Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Mariana Trench, Gulf of Mexico |
Despite the many advances in technology, deep-sea exploration remains a challenging and risky endeavor that presents numerous obstacles for scientists and researchers. One of the biggest challenges of exploring the deep sea is the extreme pressure that exists at great depths, which can crush submarines and other equipment if not properly designed and reinforced. In addition to pressure, deep-sea exploration also poses risks from extreme temperatures, corrosive seawater, and unpredictable currents that can make navigation difficult and dangerous.
These factors make it essential for researchers to carefully plan their expeditions and to use specialized equipment that can withstand the harsh conditions of the deep sea. Another major challenge of deep-sea exploration is the high cost and logistical complexity of conducting research in such a remote and inaccessible environment. Deep-sea expeditions require extensive planning, funding, and coordination among multiple organizations, as well as specialized vessels and equipment that are often in short supply.
Furthermore, conducting research at great depths requires highly trained personnel who are skilled in operating complex machinery and conducting scientific experiments in challenging conditions. These factors make deep-sea exploration a costly and resource-intensive endeavor that requires careful management and collaboration among scientists, engineers, and government agencies.
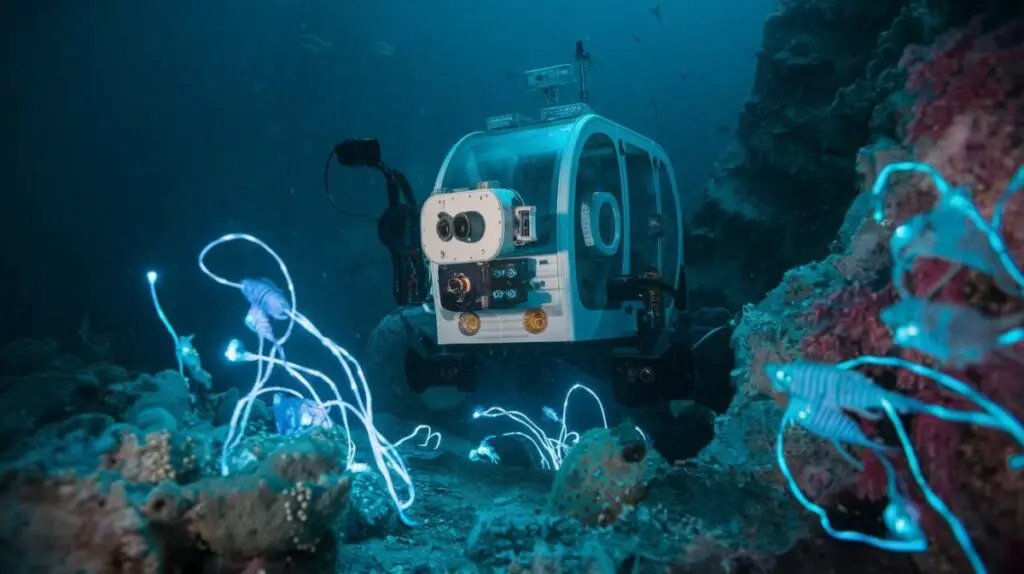

The Importance of Deep-Sea Exploration for Scientific Research
Deep-sea exploration plays a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and understanding of the ocean’s depths, as well as its impact on the planet as a whole. The deep sea is home to a vast array of unique ecosystems that are poorly understood but are believed to play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate and supporting marine life. By studying these ecosystems, scientists can gain valuable insights into how they function, how they are being affected by human activities, and how they can be protected for future generations.
Deep-sea exploration also provides important data on ocean circulation, nutrient cycling, and other processes that are essential for understanding global climate patterns and predicting future changes. In addition to its scientific value, deep-sea exploration also has practical applications for human society, such as in the fields of medicine, energy production, and resource management. Many marine organisms found in the deep sea produce unique compounds that have potential applications in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and other industries.
By studying these organisms, scientists can discover new drugs, materials, and technologies that could benefit human health and well-being. Furthermore, the deep sea is believed to hold vast reserves of minerals, oil, and gas that could be exploited for energy production in the future. By conducting research in these areas, scientists can help to ensure that these resources are managed sustainably and responsibly for the benefit of society.
Environmental Impact of Deep-Sea Exploration
The Fragility of Deep-Sea Ecosystems
The deep sea is an extremely fragile environment that is home to many species that are highly adapted to its unique conditions, such as high pressure, low temperatures, and limited food sources. The use of Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs), Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), and other equipment in deep-sea exploration can disturb these delicate ecosystems by stirring up sediment, damaging corals and other fragile organisms, or introducing invasive species from other parts of the ocean.
Potential Impacts on Marine Life
Furthermore, the collection of samples from the deep sea can have negative effects on local populations by disrupting their natural habitats or removing key species from the ecosystem. In addition to direct impacts on marine life, deep-sea exploration also raises concerns about pollution from equipment, fuel spills from research vessels, and other sources of contamination that can harm ocean ecosystems. The noise generated by underwater vehicles can also disrupt marine mammals and other animals that rely on sound for communication and navigation.
The Need for Responsible Exploration
These environmental impacts highlight the need for careful planning and regulation of deep-sea exploration activities to minimize harm to marine life and ensure that research is conducted in a responsible manner. By implementing best practices for environmental stewardship and conservation, scientists can help to protect the delicate balance of life in the deep sea while still advancing our understanding of this important ecosystem.
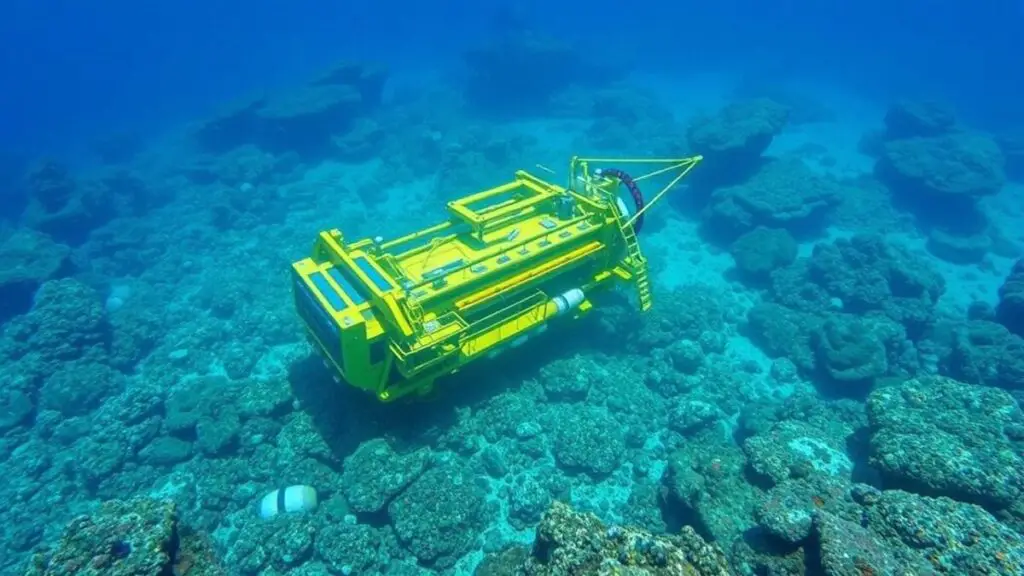

Future Prospects and Innovations in Deep-Sea Exploration
Looking ahead, deep-sea exploration holds great promise for continued discoveries and innovations that will expand our knowledge of this enigmatic realm. Advances in technology are making it possible to explore deeper into the ocean than ever before, using new types of vehicles such as submersibles, manned submarines, and advanced diving suits that can withstand extreme pressures. These technologies will allow scientists to access areas of the ocean that were previously inaccessible and to conduct more detailed studies of marine life, geology, and other aspects of the deep sea.
In addition to new vehicles, researchers are also developing advanced sensors, imaging systems, and sampling tools that will provide valuable data on the ocean’s depths. Another area of innovation in deep-sea exploration is the development of new research methods and interdisciplinary approaches that bring together experts from different fields to study complex problems in marine science. By combining expertise in biology, geology, chemistry, physics, engineering, and other disciplines, scientists can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how the deep sea functions as an interconnected system.
This holistic approach will help to address key questions about biodiversity, ecosystem dynamics, climate change impacts, and other pressing issues facing the ocean today. Furthermore, advances in data analysis and modeling will allow researchers to integrate large datasets from multiple sources to create more accurate predictions about future changes in the deep sea. In conclusion, deep-sea exploration offers a fascinating glimpse into an alien world that holds countless mysteries waiting to be uncovered.
Through recent discoveries and cutting-edge technologies, scientists are gaining new insights into the biology, geology, ecology, and history of the ocean’s depths. While there are challenges and risks associated with exploring such a remote environment, the importance of deep-sea exploration for scientific research cannot be overstated. By studying this enigmatic realm, researchers can gain valuable knowledge about marine ecosystems, global climate patterns, resource management strategies, and potential applications for human society.
As we look to the future, continued innovation in deep-sea exploration will lead to even greater discoveries that will expand our understanding of this vital part of our planet’s natural heritage.
Hooked on Tech: Exploring the latest Fishing Gadgets that Anglers swear by.
In the realm of angling, where tradition and technology often converge, a new wave of fishing gadgets has emerged, transforming the way anglers approach their craft.
From advanced fish finders to smart bait systems, these innovations have not only revolutionized the fishing experience but have also garnered a loyal following among anglers worldwide.
Goture Fishing Tool Kit, Fishing Pliers, Fillet Knife with Sheath, Fish Lip Gripper, Fish Hook Remover, Lanyard, Line Scissors, Sharpener, Stainless Steel Soap, Saltwater Gear Kit, Gifts for Men
$35.99 (as of October 8, 2025 08:42 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)KastKing Brutus Fishing Net, Foldable Extendable Fish Landing Net, Lightweight & Portable Fishing Net with Soft EVA Foam Handle, Holds up to 44lbs/20KG, Fish-Friendly Mesh for a Safe Release
$39.99 (as of October 8, 2025 09:36 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Stren Original Monofilament Fishing Line
$3.73 (as of October 8, 2025 17:22 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)RAWILL Fishing Kit,Filleting Knife, Hook Remover, Fish Grip, Line Cutter,Fishing Scale, Pliers with Lanyards,Not Include Batteries.As A Gift for Anglers
$23.99 (as of October 8, 2025 11:13 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Berkley Trilene XL Monofilament Fishing Line
$8.97 (as of October 8, 2025 19:41 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Minnow Trap 32in*10in” with Foldable Fishing Net & Collapsible Fish Bucket – Crab, Crawfish, Shrimp Trap for Freshwater Saltwater Fishing
$15.99 (as of October 8, 2025 11:13 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)KCMOSGI 12 Pcs Fishing Bells,Fishing Pole Bells,Catfishing Equipment,for Fishing Bells for Rods
$9.99 (as of October 8, 2025 11:13 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)BAIKALBASS Braided Fishing Line 4 Strands Stronger Multifilament PE Braid Wire for Saltwater 6LB-100LB 110yards 328yards 547yards Super Strong Superline
$9.99 (as of October 5, 2025 16:39 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)RoundFunny 14 Pcs Fishing Tool Kit, Fillet Knife, Fishing Pliers with Lanyard, Digital Scale, Lip Gripper, Hook Remover, Fish Scaler, Braid Scissors, Gloves, Sharpening Rod, Tool Retractor, Towel Bag
$37.99 (as of October 8, 2025 08:42 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)TIDEWE Bootfoot Chest Wader, 2-Ply Nylon/PVC Waterproof Fishing Hunting Waders with Boot Hanger for Men Women Green Brown
$42.98 (as of October 8, 2025 19:41 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Fish Corner Swimbait Jig Heads Fishing Jigs Swim Bait Jighead with Two Bait Keepers and 3D Eyes 1/8 3/16 1/4 3/8 1/2oz Jigheads Freshwater Saltwater Fishing
$9.99 (as of October 8, 2025 09:36 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Dovesun Crappie Jig Heads for Fishing Underspin Jig Heads for Crappie Walleye Bluegill Ice Fishing 20pcs/25pcs 1/32oz, 1/16oz, 1/8oz
$9.99 (as of October 6, 2025 21:34 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)6th Sense Bodega Creature Bait – 3.5″, 4.8″, 6.5″ Soft Plastic Craw multi-pack for Bass Fishing – Flipping, Pitching, Jig Trailer, Carolina Rig and more
$6.99 (as of October 8, 2025 09:36 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)mpeter 9 Strands 8 Strands 4 Strands Armor Braided Fishing Line, 100/300/500/1000 Meters Abrasion Resistant Braided Lines, High Sensitivity and Zero Stretch, with Smaller Diameter
Now retrieving the price.
(as of October 5, 2025 16:39 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)