Interpreting Fish Behavior That Grabs Our Attention, We are analyzing fish behavior that captures our interest. Fish have always captivated human attention with their vibrant scales and beautiful motions.
But what does their wet world conceal from view?
This article delves into the complexities of fish behavior, examining the science, social structures, communication, and other aspects that influence the fascinating behaviors of our aquatic companions.
A complex network of sensory perceptions, environmental adaptations, and instincts explain fish behavior.
Fish have a variety of senses to help them traverse their environment. Their excellent vision helps with this, while their lateral lines detect minute changes in water pressure, which helps them identify potential predators.
Environmental factors such as temperature, water quality, and the availability of food sources influence the behavior of these incredibly adaptive animals.
Fish use an amazing variety of signals to communicate, ranging from complex chemical cues to aggressive visual displays.
Fish communities include a variety of social systems, from solitary species to highly structured schooling behavior, where coordinated movements shield the species from predators.
Analyzing these social interactions shows how aquatic ecosystems are intricately balanced.
Brushless RC Boat 40+MPH, Remote Control Boat for Adults Kids Enthusiasts

The Science Behind Fish Behavior
Fish behavior is based mostly on their instincts and survival strategies; it is not random.
Understanding how environmental circumstances affect their behavior can provide insight into the undersea drama that unfolds every day.
Fish’s complex dance in their watery environments is an expression of millions of years of evolutionary adaptation.
Temperature, water quality, and the availability of food sources all have a significant impact on them.
For instance, some species migrate in response to seasonal variations because nature forces them to select the optimal environments for reproduction and nutrition.
Furthermore, it’s fascinating to see the social structures found in fish groups.
Schools create hierarchies and complex communication networks that increase their chances of surviving as a group.
Fish’s color and body language are more than just decorative elements; they are essential for intimidation, concealment, and communication.
Fish may also undergo behavioral adaptations in response to environmental changes, such as variations in water temperature or pollution levels, as they attempt to adjust to their new surroundings.

Communication Among Fish
Although we may think of fish as silent creatures, they have a complex communication system that goes against what we initially thought.
In their colonies, auditory cues, visual cues, and even smells are important means of information transmission.
Fish species engage in an elaborate dance of communication under the calm surface of aquatic settings.
They use visual cues, including body language, color changes, and fin displays, as a dynamic language to communicate a range of emotions, establish their authority, and start courting rituals.
Furthermore, pheromones deliver chemical cues that allow fish to communicate without making direct physical contact.
These chemical signals transmit important information about reproductive readiness, territorial borders, and even potential threats.
As a result, the underwater environment is full of unseen dialogues, in which fragrances facilitate complex interactions amongst its residents.
Unexpectedly, a wide variety of fish species can make noises, from pops and clicks to intricate vocalizations.
In addition to luring mates, these audio cues also operate as a deterrent to predators and facilitate group mobility.
The symphony of aquatic noises, often undetectable to human ears, vividly illustrates the complex communication network functioning under the waves.

Social Structure in Fish Communities
Fish communities do not lack social systems with leadership positions and hierarchies, despite common notions to the contrary.
Examining these relationships reveals the complexities of their collective actions.
Different fish species create complex social structures in these watery communities, dispelling the myth that fish are instinctive animals.
Clownfish and cichlid observations demonstrate the existence of dominant individuals that are essential to resource allocation and decision-making.
These leaders guide the group through activities like hunting and navigating the environment; you can often identify them by their aggressive posturing or courtship displays.
Furthermore, research has revealed that some fish have exceptional problem-solving skills, suggesting a higher cognitive ability than previously believed.
These results cast doubt on the conventional understanding of fish as passive, lonesome creatures.
Fish communities have social structures that are not only functional but also suggest the emergence of sophisticated communication systems.
Body language, vibrational cues, and even color changes influence the complex web of relationships among group members.
Fish communities are dynamic, sensitive, and worthy of more scientific investigation to fully understand the complexities of their social behaviors as our understanding of their social lives grows.

Reproductive Behavior
Fish display a wide variety of reproductive activities that help ensure the survival of their species, from complex mating rituals to parental care.
These remarkable adaptations have shaped fish reproductive methods over millions of years in response to their habitats.
Fish species engage in captivating displays of colors, patterns, and coordinated movements during courtship rituals to attract potential mates and establish dominance within their community.
The complexity of fish behaviors reflects their diverse habitats, which include freshwater streams and coral reefs.
Another important part of fish reproduction is parental care, where different species have different ways of making sure their young are okay.
While some fish construct elaborate nests or carry growing embryos in their mouths, others carefully secure their eggs.
The delicate juvenile fish have a far higher chance of surviving thanks to the parental investment, which also shields them from predators and gives them a better start in life.
Overall, the wide range of reproductive activities seen in fish highlights how incredibly adaptive these watery animals are.
The study of fish reproduction provides us with important insights into the delicate balance that supports aquatic ecosystems all around the world, as well as a deeper understanding of fish’s evolutionary past.
Brushless RC Boat 40+MPH, Remote Control Boat for Adults Kids Enthusiasts
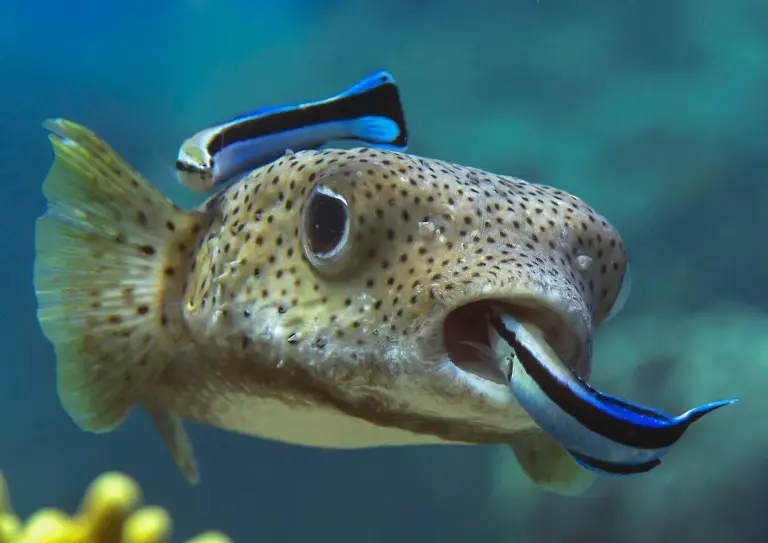

Adaptations for Feeding
How do fish find prey? Which foods do they prefer to consume?
Deciphering the means by which they sustain themselves exposes the intriguing realm of predator and survivor.
The species, environment, and availability of prey influence the wide range of hunting strategies used by fish.
In order to identify movement and vibrations in the water, predatory fish frequently rely on their excellent senses, including sight and lateral lines.
Certain animals, such as the expert pike, pursue their prey slowly, using slow, deliberate movements and concealment to approach before making an astonishingly rapid strike.
Others, such as groupers, use an ambush tactic, lurking behind coral formations or cracks and waiting for gullible prey to swim past.
Furthermore, certain fish engage in coordinated hunting behaviors. This includes well-known tuna hunting groups and deliberate dolphin encirclement.
There is a vast range of feeding habits; herbivores nibbling on algae and carnivorous predators that hunt smaller fish are only two examples.
This complex dance between predator and prey demonstrates the fish’s flexibility and resourcefulness in their never-ending search for food and survival in the watery world.
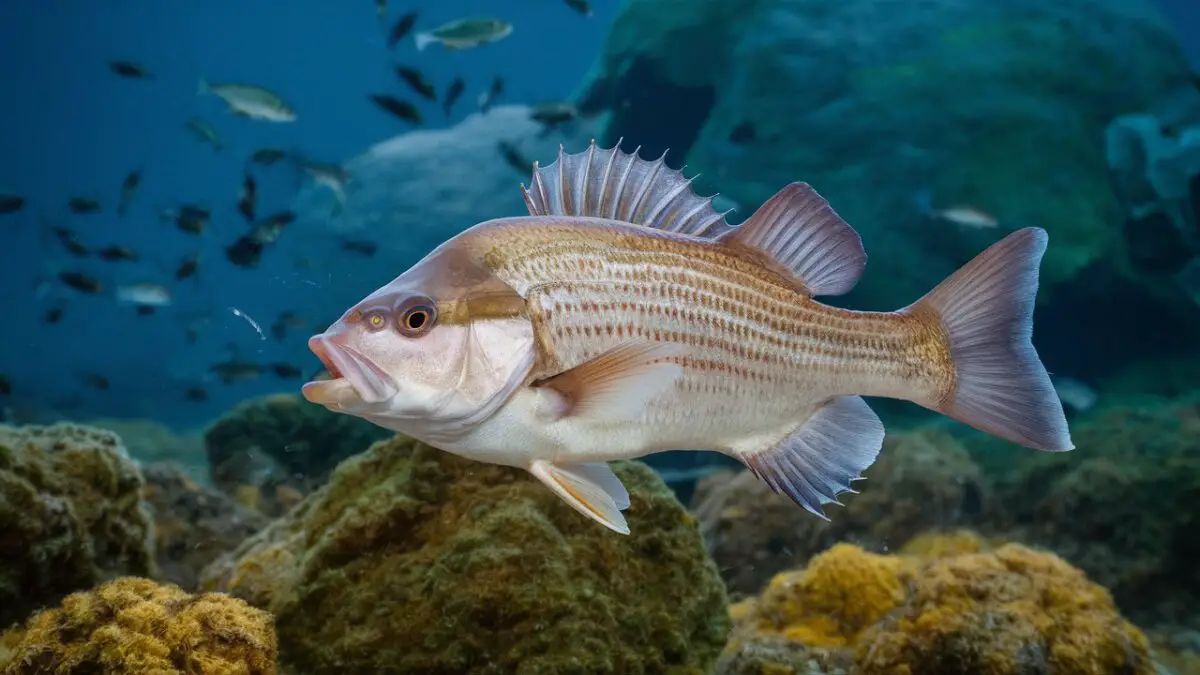

Migratory Patterns
Many fish species’ seasonal migrations are closely linked to their life cycles and environmental factors.
Numerous variables, from changing environmental conditions to reproductive needs, are driving these migratory patterns.
Salmon, for example, migrate in a way that is quite amazing. Their instinct to reproduce in their birthwaters drives them from freshwater spawning grounds to the open ocean and back.
Their migration paths are quite precise because of factors such as temperature, water currents, and even astronomical signals.
These motions have enormous ecological implications because they affect nutrient cycling in many ecosystems and control population dynamics.
The interconnection of these migrations highlights the intricate dance between species and their habitats, underscoring the fragile balance of nature.
It is essential to comprehend and protect these migratory patterns if aquatic ecosystems are to remain resilient and healthy globally.

Human Interaction and Impact
When people interact with aquatic habitats, fishing methods and environmental changes may significantly impact fish behavior.
The rising demand for seafood has led to overfishing, which disturbs natural ecosystems and reduces fish populations, affecting fish migration and reproductive cycles.
Furthermore, pollution and warming water temperatures put aquatic environments under additional stress and have an impact on fish physiology.
Examining these linkages highlights the critical need for sustainable fisheries management and environmental protection while also illuminating the complex web of relationships found within aquatic ecosystems.
Knowing can create well-informed plans to reduce adverse effects, protect biodiversity, and maintain the long-term health of our seas by knowing how human activity affects fish behavior.
With this information, communities, decision-makers, and environmentalists may make wise choices that strike a balance between meeting human needs and protecting delicate aquatic ecosystems.
Interpreting Fish Behavior That Grabs Our Attention

Aquarium Enthusiasts’ Perspective
Understanding and witnessing fish behavior in captivity provides aquarium owners with a unique perspective on their innate inclinations and strengthens the bond between people and aquatic life.
A deep understanding of a fish’s intricate social structures and instincts develops when one learns about the nuances of their daily routines, from their schooling patterns to their unique eating habits.
The aquarium setting is a microcosm that mimics the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems in addition to being a stunning display of underwater beauty.
It makes enthusiasts think about the accountability involved in preserving a healthy ecosystem and supporting sustainable behaviors and conservation initiatives.
Because of this close relationship, aquarium keepers may actively contribute to the preservation of many species and become stewards of aquatic well-being.
As a result, the collaborative process of monitoring and tending to the confined fish improves not only their quality of life, but also the satisfaction and enrichment of the people who maintain these underwater environments.
Common Misconceptions About Fish Behavior
It’s critical to debunk misconceptions and prejudices about fish behavior in order to promote true knowledge and respect for these animals.
Fish, in contrast to popular belief, have sophisticated social structures, sophisticated communication techniques, and exceptional problem-solving abilities.
By dispelling myths that depict fish as lifeless and indifferent, we open the door to a more sophisticated understanding of their emotional and cognitive abilities.
Research on fish behavior is still revealing their rich tapestry, which includes their capacity to build complex social ties and adapt to a variety of situations.
This new information dispels myths and promotes a change in the public’s attitude toward fish as sentient creatures deserving of ethical treatment and respect.
Recognizing fish’s cognitive skills helps us appreciate their place in aquatic ecosystems and reevaluate our role in protecting fish welfare both in the wild and in captivity.

Technological Advances in Studying Fish Behavior
Technological developments, such as sensors and tracking devices, have completely changed how we can research fish behavior.
The essay examines how these instruments offer hitherto unheard-of insights into the complex lives of aquatic animals.
Scientists can now observe fish movements with unprecedented accuracy thanks to tracking tools such as satellite tags and acoustic transmitters.
These gadgets provide up-to-date information on feeding schedules, breeding patterns, and migration patterns, illuminating hitherto unknown facets of animal existence.
Furthermore, advanced sensors are able to assess environmental parameters like salinity and temperature in the water, giving researchers a thorough grasp of the elements affecting fish behavior.
This abundance of data has applications for fisheries management and conservation initiatives, in addition to furthering our scientific understanding of marine ecosystems.
Through technological innovation, researchers may solve the enigmas surrounding fish behavior and make well-informed judgments that will preserve aquatic habitats for coming generations.

Conservation Efforts Based on Understanding Fish Behavior
Maintaining fish habitats and encouraging sustainable fishing methods require a thorough understanding of fish behavior.
This understanding is the foundation for successful conservation initiatives. Scientists are able to determine important breeding areas, migration patterns, and eating preferences by examining the subtleties of fish behavior.
Equipped with this knowledge, conservationists can put focused tactics into place to safeguard these crucial regions and guarantee the survival of fish populations.
Furthermore, we can develop ethical fishing methods that have the least negative effects on the ecosystem by understanding the behavioral ecology of various fish species.
For instance, gear adjustments based on behavioral insights or the implementation of seasonal fishing regulations can prevent overexploitation.
In addition to protecting fish habitats, this cooperative approach combining scientific knowledge and conservation action promotes a long-term equilibrium between human requirements and the preservation of aquatic ecosystems.
Essentially, when behavioral information guides conservation efforts, they become more sophisticated and successful in preserving the delicate balance of our freshwater and ocean habitats.

The Influence of Temperature on Fish Behavior
Temperature significantly influences fish behavior, determining their food preferences, migratory patterns, and reproductive activity.
Deciphering the subtleties of seasonal temperature fluctuations is essential to understanding the complex dynamics seen in aquatic settings.
Fish adjust to temperature changes by moving to areas with the best thermal conditions for survival.
Furthermore, it is critical to investigate how climate change affects aquatic ecosystems.
As a result of climate change, rising temperatures present serious problems for fish populations.
It can lead to the introduction of invasive species, alter the availability of suitable habitats, and disrupt the timing of crucial life cycle events.
The interaction of temperature, seasons, and climate change threatens the complex web of life below the water’s surface, highlighting the delicate balance within aquatic ecosystems and the need for extensive study and conservation efforts.
30M/100FT Portable Underwater Fishing Camera Video Fish Finder with Drop Protection

Case Studies: Remarkable Fish Behavior Stories
Showcasing particular instances of remarkable fish behavior demonstrates the variety and intricacy of behaviors seen in many species.
Consider the archerfish, which is renowned for its incredible hunting strategy.
This species exhibits remarkable accuracy and precision as it spits water jets at insects that are above the water’s surface.
The coral grouper and the huge moray eel’s cooperative hunting habits are another amazing example.
In the animal realm, interspecies cooperation is unusual; however, these two different species work together when seeking food on coral reefs.
Furthermore, the remarkable migratory voyage of Atlantic salmon serves as an example of the tenacity and navigational skills of some fish species.
These fish display tenacity and innate behavior as they overcome numerous hurdles on their journey back to their natal spawning grounds over large distances.
These varied illustrations highlight the amazing variety of actions that add to the vibrant fabric of aquatic life.

Conclusion
In summary, understanding fish behavior entails exploring a fascinating and complex environment.
This investigation expands our understanding of the varied and extraordinary lives led by our aquatic counterparts, from the science underlying their behavior to the effects of human engagement.
The intricacy of their communication, mating rituals, and migratory patterns reveals a complex web of ecological interactions crucial to maintaining the delicate balance of marine environments.
Furthermore, the realization of the effects of human activity, such as pollution and overfishing, heightens the urgency of our duty to protect the seas as stewards of life.
It is clear that protecting fish habitats and encouraging sustainable behaviors is not just an ecological need but also a moral one, as we appreciate the complexity of fish behavior.
Driven by the interdependence of all living forms in our planet’s vast aquatic domains, we set out on an ongoing journey of enlightenment to uncover the mysteries beneath the surface of the water.
Do fish have emotions?
Fish exhibit behaviors indicative of responses to stimuli, but the extent to which they experience emotions is still a subject of scientific debate.
Can fish recognize individual humans?
Research suggests that some fish, particularly those in captivity, can learn to recognize and interact with individual humans.
How do environmental changes affect fish behavior?
Changes in water temperature, pollution, and habitat destruction can significantly impact fish behavior, leading to alterations in migration patterns and feeding habits.
Why do some fish travel long distances during migration?
Fish undertake long migrations for various reasons, including finding suitable breeding grounds, following food sources, and avoiding predators.
What can aquarium enthusiasts do to promote responsible fishkeeping?
Aquarium enthusiasts can contribute to responsible fishkeeping by choosing sustainable species, providing adequate space and enrichment, and supporting conservation initiatives.
Hooked on Tech: Exploring the latest Fishing Gadgets that Anglers swear by.
In the realm of angling, where tradition and technology often converge, a new wave of fishing gadgets has emerged, transforming the way anglers approach their craft.
From advanced fish finders to smart bait systems, these innovations have not only revolutionized the fishing experience but have also garnered a loyal following among anglers worldwide.
Plano 3-Tray Tackle Box with Dual Top Access, Dark Green Metallic/Off White, Premium Tackle Storage
$18.99 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)YLINSHA Fishing Knife,Fish Cleaning Kit 7 PC set Fish Knife, Fish Scale Cleaning Brush, multi-functional Scissors, anti-cutting Gloves, Fishbone Tweezers, storage Bag
$19.99 (as of November 18, 2025 10:29 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)PLUSINNO Floating Fishing Net for Steelhead, Salmon, Fly, Kayak, Catfish, Bass, Trout Fishing, Rubber Coated Landing Net for Easy Catch & Release, Compact & Foldable for Easy Transportation & Storage
$38.99 (as of November 18, 2025 02:23 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)MELASA Winter Fleece Lined LED Beanie, USB Rechargeable Hand Free Warm Hat with Light Built in, Gifts for Men Dad Husband Him
$9.99 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Movtovic 70 Pcs Corrosion Resistance Fishing Swivels & Snaps, 7 Sizes Detachable Snap Swivels, Convenience Pack Swivels Fishing Tackle for Recreational Fishing
$4.29 (as of November 18, 2025 22:28 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Clear Fishing Wire,755FT Monofilament Fishing Line,Clear String for Hanging,Strong Wire Invisible Nylon Thread for Hanging Balloon,Garland,Picture,Crafts,Decorations,Suitable for Beading Sewing
$4.59 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)New 2Pcs Fishing Bite Alarm, Upgrade Sensitive Electronic Fishing Alarms ,Sound Bite Alert Bell with LED Lights,Fish Bite Alarm Indicator Suitable for Various Fishing Scenes
$10.50 (as of November 18, 2025 22:28 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)KastKing Bully Wooly Convertible Mittens – Premium Wool Fingerless Fishing Gloves with Magnetic Flip-Top, Fleece Lining, Non-Slip Grip, Extra-Long Cuff, 4-Way Stretch, Cold Weather Winter Gear
$31.49 (as of November 18, 2025 22:28 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)pullther fishing Fish Gripper 9.2″,Muti-Function Line Cutter and Split Ring Fishing Pliers for Fly Fishing, Ice Fishing,Saltwater Fishing Tool Kit,Fishing Gear with Fishing Lanyard
$9.99 (as of November 18, 2025 10:29 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)RUNCL Fishing Plier, Fish Lip Gripper Kit, Fishing Remover Extractor, Multi-Function Fishing Tools for Saltwater, Freshwater, Ice Fishing, Premium Fishing Gifts for Men
$9.10 (as of November 18, 2025 22:28 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Nomad Design DTX Minnow with Patented Autotune System – Distressed Baitfish Swimming Action, BKK Diablo
$49.99 (as of November 18, 2025 22:28 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)RESTCLOUD Fishing Landing Net with Telescoping Pole Handle, Fishing net Freshwater for Kids Men Women, Extend to 40-63 Inches
$14.99 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)AnglerCo Imposter Jig – Pinfish Color Slow Pitch Flutter Jigging Lure for Saltwater – Inshore & Offshore Fishing Spoon for Snapper, Grouper, Tuna, More
$18.99 (as of November 17, 2025 06:42 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)TRUSCEND Pre-rigged Fishing Jig Lures for Freshwater and Saltwater, Innovative Super Durable TPE Bass Lures, Lifelike Shrimp Crayfish Swimbait, Weedless Lure for Crappie Trout Walleye, Keep Separately
$19.99 (as of November 18, 2025 04:59 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Yamamoto Senko Soft Plastic Worm Easy to Use Bass Fishing Stick Bait Lures
$6.79 (as of November 18, 2025 22:28 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Clear Fishing Wire,755FT Monofilament Fishing Line,Clear String for Hanging,Strong Wire Invisible Nylon Thread for Hanging Balloon,Garland,Picture,Crafts,Decorations,Suitable for Beading Sewing
$4.59 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)PLUSINNO Fishing Lures, 137Pcs Tackle Box with Tackle Included, Crankbaits, Spoon, Hooks, Weights & Other Accessories, Fishing Bait Lure Gear Kit Gift for Men Bass Freshwater
$15.27 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)KastKing SteelStream 6pc Fishing Tool Kit – Corrosion Resistant Fishing Pliers with Lanyard, Fillet Knife, Floating Fish Lip Gripper, Fishing Braid Scissors, Tool Retractor, Fishing Gifts for Men
$27.19 (as of November 18, 2025 04:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)LUCKY CRAFT FlashMinnow 125 YAWARA, Saltwater Fishing Lures, Jerkbait Surf Fishing Accessories and Gear, Halibut and Bass Fishing Lures
$9.99 (as of November 17, 2025 06:42 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Berkley Hit Stick Fishing Hard Bait
Now retrieving the price.
(as of November 18, 2025 23:58 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)